It is a known fact that cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, coronary heart disease, etc., can cause serious health risks. When it comes to heart failure and heart attack, both medical conditions are related but are not the same. Oftentimes, people get confused with these two terms and use them incorrectly. While the causes and effects of both conditions are the same, they are distinct health issues. Let us understand how heart failure and heart attack differ from one another.
What is the Difference Between Heart Failure and heart attack?
Heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, is a chronic medical condition. This means that this issue develops slowly over a long period. Heart failure is said to occur when the heart muscle fails to pump enough blood to meet the demands of the body. Narrowed coronary arteries with high blood pressure make the heart weak, blocked or stiff due to which there is improper pumping of blood.
A heart attack occurs due to the blockage of arteries by fatty deposits known as plaques. Formation of blood clot due to the rupture of plaques further blocks the arteries. This may often lead to a heart attack. It is also known as myocardial infarction that occurs suddenly. In some cases, parts of the heart muscles die due to lack of blood supply. This health condition can be fatal if immediate medical attention is not available for the patient.
What are the causes of Heart Failure and Heart Attack?
Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle is weak or stiff. Listed below are the causes of heart failure:
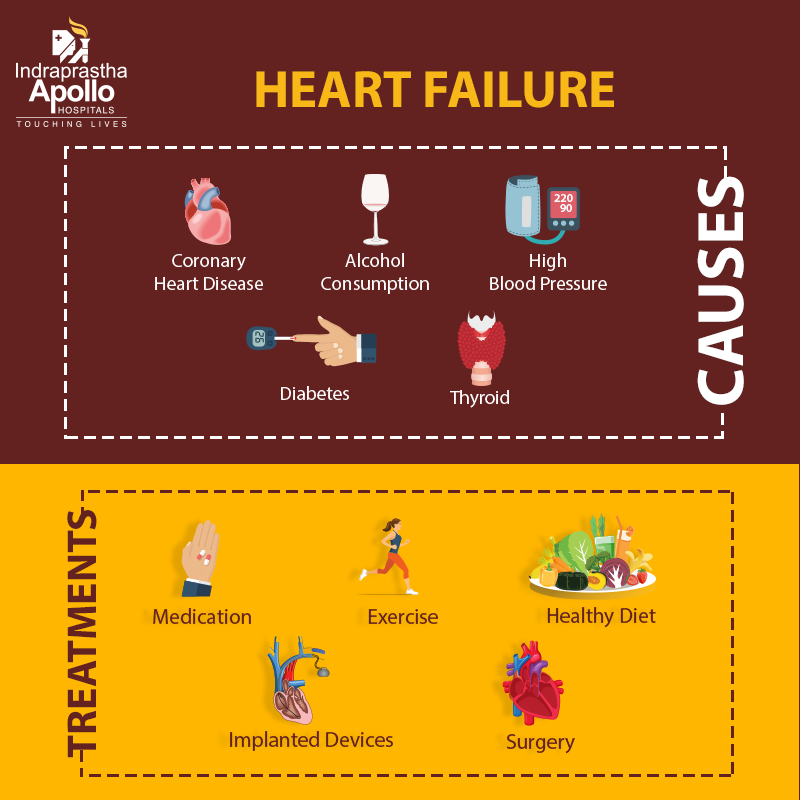
- Coronary artery disease: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common form of heart disease in which cholesterol and fatty deposits get accumulated in the heart arteries affecting the blood flow to the heart muscles. This causes chest pain, also termed as angina, and over time causes heart failure.
- History of heart attack (myocardial infarction): An individual with a history of a heart attack may have an increased risk of her/his heart muscle getting damaged again. This further affects the ability to pump enough required in the body.
- High Blood pressure: If a patient has unregulated high blood pressure, her/his heart has to pump blood harder than normal to ensure blood circulation. This weakens the heart over time and may lead to heart failure.
- Abnormal heart valves: Heart valve abnormalities can be congenital caused by infection or any other heart disease. The heart muscle has to pump harder to ensure blood circulation because the valves do not open or close completely, thus, resulting in heart failure.
- Heart muscle disease: Diseases such as dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or myocarditis (inflammation) caused by certain infections, excessive alcohol consumption or drug abuse can damage the heart muscle and increases the risk of heart failure.
- Congenital heart disease: Some patients have birth defects in the heart or its chamber while the rest of the muscle is healthy. In such cases, the heart has to work harder than usual to pump blood due to which the chances of a heart failure are increased.
- Lung disease: When an individual is suffering from severe lung disease, the pressure on the heart to ensure proper oxygen supply to the rest of the body is increased drastically. As the heart works harder, the chances of heart failure are higher.
- Diabetes: A diabetic patient is more prone todevelop hypertension and atherosclerosis due to elevated lipid levels in the blood, hence increasing the risk of heart failure.
- Obesity: The heart of an obese person has to work harder than a person with ideal body weight. Moreover, obesity leads to sleep apnoea and cardiomyopathy that contribute to increased heart failure risk.
- Other factors: There are other factors responsible for heart failure like:
- Anemia, low red blood cell count causes cardiac stress as the heart has to work harder to carry oxygen to the body by rapidly moving a smaller number of cells.
- Hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid gland causes the body to work at a faster pace, hence the heart has to work faster, gradually leading to a weak heart.
- Abnormal heart rhythm means irregular heartbeats. As this occurs, the heart is unable to pump the required quantity of blood in the body.
On the other hand, a heart attack occurs due to the blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle. Following are the causes of blockage:
- Atherosclerosis: Narrowing of coronary arteries due to build-up of the fatty substance (plaque). The rupture of plaques can further cause a blood clot causing coronary artery blockage.
- Coronary artery spasm: This is the sudden narrowing or stiffness of the coronary artery due to smoking, cold weather, or extreme stress.
- Coronary artery dissection: Separation of the inside wall of the coronary artery, which further causes blockage of blood flow.
- Obesity
- Smoking or an unhealthy lifestyle
What are the symptoms of Heart Failure and Heart Attack?
Some of the common symptoms of heart failure are:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Sleep disturbance/apnoea
- Edema (swelling) in legs, ankles, and feet
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
Symptoms of heart attack vary from person to person and differ for men and women. These include:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Pain in the jaw, upper body, like arms, back, etc.
- In some cases, pain radiates to the legs
- Anxiety
- Breathing difficulty
- Fatigue, nausea, vomiting
- Feeling cold or sweating
What are the treatments for heart failure and heart attack?
Treatment for heart failure is lifelong but with the right approach the symptoms can improve and the heart muscle can be strengthened. Treatment options for heart failure are:
- Medication to lower blood pressure, normalize the heartbeat, reduce edema, manage breathing problems, etc.
- Surgery can be suggested based on your condition:
- Coronary artery bypass surgery: To ensure blood flows freely.
- Heart valve repair or replacement.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs): A device to ensure a normal heartbeat.
- Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT), or Biventricular pacing: A device to ensure proper pumping of blood.
- Heart Transplant: In a case of severe heart failure that is not responding to any medication or surgery, a heart transplant is recommended.
A heart attack needs immediate medical attention as each minute counts because restoring blood flow is important to prevent heart damage. Treatment options for heart attack are:
- Medication is given to prevent further blood clots and to restore blood flow.
- Medication to lower and control cholesterol, blood pressure, and anxiety.
- Surgical procedure might be recommended based on your condition:
- Coronary angioplasty and stenting: It is also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in which the blockage is removed and the blood flow is restored. Along with this, a stent is placed to keep the vessel intact.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery: Bypass surgery can be recommended after a few days of the heart attack or an emergency bypass surgery can be planned at the time of heart attack. This is to ensure that the blood flow is restored.
Both heart failure and heart attack are serious forms of heart conditions and both need to be treated by experienced specialists and surgeons. The causes of heart failure and heart attack are similar but the consequences can vary from one patient to another. Heart failure happens gradually over some time while a heart attack is sudden and unexpected.